It will be so helpful to know what malaria is and how to treat and prevent it. The more knowledge you have about malaria the better you will be able to prevent it for a healthy life.
WHAT IS MALARIA?
Malaria is a dangerous disease spread by the bite of an infected Female Anopheles Mosquito. It leads to death if not diagnosed and treated on time. Malaria affects any age range, from neonates(from birth to one month) to adults.
WHAT CAUSES MALARIA?

Malaria is caused by a plasmodium parasite carried by a Female Anopheles Mosquito. The human body serves as host to the plasmodium parasite.
The infected female Anopheles Mosquito bites and sucks blood from the human body to nurture its eggs, causing a transfer of an immature form of plasmodium parasite into the blood of the human body (host).
HOW DOES THE PLASMODIUM PARASITE AFFECT THE BODY?

The immature form of plasmodium parasite moves to the liver after entering the blood to mature. The mature plasmodium parasite then enters the blood again to attack the red blood cells where the parasite multiplies rapidly inside the red blood cells.
The number of the plasmodium parasite increases causing the red blood cells to burst releasing numerous matured plasmodium parasite into the blood. The plasmodium parasite continues to attack the red blood cells. The cycle continues until the host develops the signs and symptoms.
Note: the red blood cells contain hemoglobin which is responsible for transporting oxygen to the body cells and tissues. When the red blood cells are destroyed, the cells and tissues will be deprived of oxygen leading to death. The cells and tissues of the human body needs oxygen for energy and growth.
WHAT ARE THE TYPES OF PLASMODIUM PARASITE?
There are several species of malaria. Out of these species only 5 causes malaria in humans. The remaining species affect birds, monkeys, livestock, rodents, and reptiles. The five species that affect humans are: Plasmodium falciparum, Plasmodium vivax, Plasmodium ovale, Plasmodium malariae, Plasmodium knowlesi (newly discovered plasmodium strain).
WHAT IS THE INCUBATION PERIOD OF PLASMODIUM PARASITE?
Incubation period of malaria is the period between the time the infected female Anopheles Mosquito bites the host and the emergence of the signs and symptoms in the host. The incubation period for malaria ranges from one week to one year. This applies to all the plasmodium parasite above.
WHAT ARE THE SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS OF MALARIA?
The Signs and Symptoms of malaria are:










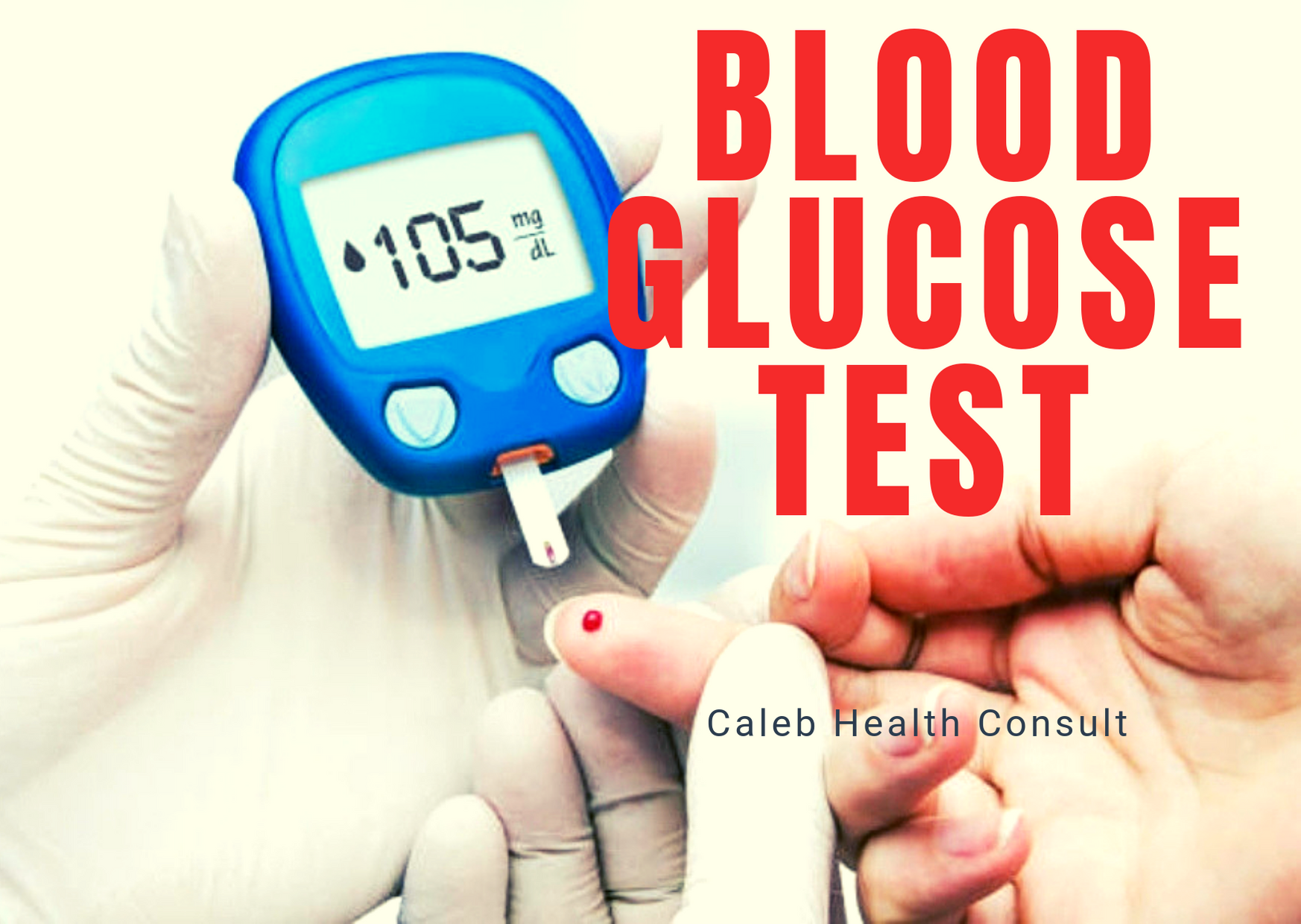
HOW IS MALARIA DIAGNOSED?

Malaria is one of the life threating diseases and must be recognized immediately to prevent mortality and the spread of the disease among the population.
This is because the infected person can be exposed to the bite of a Female Anopheles Mosquito. This causes the mosquito to be infected with the malaria parasite and when the same mosquito bites a healthy person the parasite is then transferred into the blood of the person.
Delay in the diagnosis and treatment of malaria is very dangerous. Scientists have developed diagnostic methods for the various malaria parasites.
This involves medical examination of human blood sample in a laboratory to diagnose the disease. This is mostly carried out at the hospital, registered Laboratories and Pharmacies.
In recent years, researchers have also developed a rapid diagnostic test using the rapid diagnostic test kit for the diagnosis of malaria also involves the use of human blood. These is available at the community pharmacy and also available to be purchased and used at homes.
If you notice any of the symptoms stated above kindly visit the community pharmacy or the hospital for immediate diagnosis and treatment because time is very relevant in the diagnosis as well as the treatment of malaria.
HOW DO YOU TREAT MALARIA?

Malaria must be treated as a medical emergency.
Malaria can easily kill if not treated in time. This is because after the infected female Anopheles Mosquito bites an individual, the immature plasmodium parasite that enters the blood, moves to the liver where it fully develops and then enters the blood again attacking and destroying the red blood cells.
The red blood cells are responsible for transporting oxygen to all the body parts. Lack of oxygen for some time leads to death.
Let’s look at the recommended malaria treatments for pregnant women, adult and children.
Pregnant women

Malaria affects not only the woman but the fetus as well causing birth defects such as low birth weight baby. Therefore, pregnant women ought to protect themselves from the bites of mosquitos by seeking medical attention as soon as possible.
Special clinics (antenatal clinics) in the hospital are designated for pregnant women, for medical monitoring and advice for the safety of the woman and the fetus.
It is therefore recommended for pregnant women to visit these clinics regularly. Three tablets of (sulfadoxine pyrimethamine) such as malafan, is taken once every month that is three tablets from 16 weeks( the beginning of the 2nd trimester) to before the last 4 weeks of pregnancy as a prophylactic treatment for the protection of the pregnant woman and its fetus from malaria. A total of 3- 5 doses .You stop a month before delivery.
Quinine sulfate is given if a pregnant woman is infected with the malaria parasite. Quinine sulfate or clindamycin can be used right from the first trimester.
Note: pregnant women in their second and third trimester can also take coartem after testing positive for malaria.
Adult and children
Malaria drugs are available in various doses for both adults and children. Weight is very significant in the administration of malaria drugs for effective results.
HOW DO YOU MANAGE THE SIDE EFFECTS OF ANTIMALARIAL DRUGS DURING AND AFTER TREATMENT?

The side effects of antimalarial drugs can be managed. Below are the common antimalarial side effects and how to manage them.
During treatment
Abdominal pains: analgesics commonly known as pain killers such as ibuprofen can be taken to treat the pain alongside the antimalarial drug.
Lack of appetite: appetite stimulants such as cyproheptadine preparations can be taken with the antimalarial drug in order for the patient to eat since food is important in the effectiveness of the drug.
Headaches, chills, and raised body temperatures: paracetamol can also be taken with the antimalarial drug for treatment.
Inability to sleep: cyproheptadine is sedative so it can help the patients to sleep.
Specific body pains and joint pains: pain killers such as ibuprofen can be used with the antimalarial drug.
Nausea and vomiting: promethazine can also be taken to treat the vomiting alongside the antimalarial drug. You can also manage nausea and vomiting by:
Taking your time when you eat or drink and avoiding strong smelling foods.
Dizziness and body weakness: iron or hemoglobin containing blood syrups can be used alongside the antimalarial drug.
Note: folic acid preparations should be avoided during malaria treatment because folic acid decreases the effects of antimalarial drugs or prevents antimalarial drugs from working effectively.
After treatment
Rest until you feel you have had enough rest.
Eat very well since you were not able to eat well during the treatment.
Take multivitamin syrups to boost your immune system to help your immune system recover faster.
Take blood syrups to help your body to produce more blood cells since most of the red blood cell were destroyed as a result of the infection.
Note: it is important to take this very serious because the immune system was in a fight with the plasmodium parasite and the drugs assisted the immune system to get rid of the plasmodium parasite. This makes your immune system weak. That is why you have to help your immune system to recover faster to protect your body from any other infections.
HOW DO YOU PREVENT MALARIA?

Malaria should be prevented at all times. Mosquitos are active around 6PM to 6AM. Below are the preventive measures for malaria prone countries such as Ghana etc.
Always sleep in treated mosquito nets.
These nets are treated with special insecticides to kill and repel mosquitos and other insets.
Always use mosquito repellant in the evening.
These preparation contains special chemicals to repel mosquitos and other insects.
Humans emits carbon dioxide. Through this emission, mosquitoes are able to detect the presence of humans. Mosquito repellents then acts by masking carbon dioxide emitted by the skin of humans enabling its ability to repel mosquitoes.
Always wear long sleeves and trousers in the evening.
To protect the body from the bites of mosquitos.
Get rid of the breeding places of mosquitos.
Such as stagnant water sources, unclosed trash cans, bushes, gutters, old tires etc.
Stagnant water sources.
Open cans, rubber bags, etc that are not discarded properly and left anywhere in the environment traps rain water and serves as a place for mosquitos to lay their eggs.
Therefore, it is advisable that such items are discarded properly and not left anywhere in the environment. Oil can be poured into stagnant water in pits or ditches to reduce the surface tension in water which prevents mosquitos from floating and laying their eggs. Fishes can also be introduced into such pits to feed on the mosquito larvae.
Note: surface tension is a property of water that allows objects to float in it.
Unclosed trash cans should be closed always.
Unclosed cans also collects water and serves as a bleeding place for mosquitos.
Bushes should be kept to their minimum level especially during raining season.
Water can be collected in such areas enabling mosquitos to breed.
Gutters should be kept clean always.
The water moving through gutters should not be stagnant since it can serve as a breeding place for mosquitos.
Old tires should be disposed properly if possible burned to prevent breeding grounds for mosquitos.
Water can be collected into old tires serving as a breeding grounds for mosquitos.
Use mosquito insecticides to spray your room to get rid of any hidden mosquito.
Leave your room for some time after spraying. Staying in your room just after spraying causes breathing problems and death. Insecticides kill mosquitos by dehydration (loss of water) and the same thing can also happen to you. Having enough water in your body is very essential in keeping you alive.
Spray your flower gardens with special mosquito insecticides to destroy any breeding place for mosquitos.
This is because mosquitos can breed into the water around your flower beds.
Mosquito coils are also recommended.
WHAT PRECAUTIONS ARE RECOMMENDED FOR THOSE WHO WANT TO TRAVEL TO MALARIA RISK COUNTRIES?

Precautions are important for those traveling to malaria risk countries. It could be very deadly for such individuals when they are exposed to the bite of an infected female Anopheles mosquito.
This is because their immune system has never been exposed to the plasmodium parasite before to develop some sort of immunity against the plasmodium parasite.
Such individuals can die within a short period of time if not treated with immediate effect.
Research has shown that with time those who live in malaria prone countries such as Ghana may develop immunity against the plasmodium parasite.
Below are the precautions to guide those who want to visit or migrate to malaria prone countries:
Seek medical advice if you are at risk of getting malaria in the country you are visiting.
Protect yourself from the bite of mosquitos. Ensure to always sleep in treated mosquito nets, apply mosquito repellant on your skin from 6 PM in the evening that is when mosquitos become active. Wear loose long sleeves and trousers when you want to go out from 6 PM.
Consult your Pharmacist if you can take malaria prevention tablets such as mefloquine, malarone etc based on your health status or if you are taking other drugs.
Seek medical attention immediately if you feel any signs and symptoms of malaria such as high body temperature, diarrhea, body pains and tiredness, chills, sweating, and cough.
Corresponding Author: Caleb Doamekpor, School of Pharmacy, Central University, Ghana.
Mobile: 0248391417.
Email Address: doamekporcaleb@gmail.com
Acknowledgements: This article was reviewed by Pharmacist Peace Doe, department of pharmacology and toxicology school of pharmacy Central University, Ghana, Pharmacist Ellen Anthony-Williams and Pharmacist Emmanuel Fiadzorgbe, Top Up Retail Pharmacy, Ghana.