Did you know diabetes mellitus is a major cause of blindness, kidney failure, heart attacks, lower limb amputation and stroke?
Globally an estimated 422 million adults are living with diabetes mellitus according to the world health organization (WHO) 2016.
It will be so helpful to know what diabetes mellitus is and how to manage your blood glucose level to prevent the serious problems associated with diabetes mellitus. The more knowledge you have about diabetes mellitus the better you will be able to manage it for a healthy life. I will entreat you to share this information with everyone to equip them with the necessary knowledge about diabetes mellitus and its management.
WHAT IS DIABETES MELLITUS?
Diabetes mellitus is a disease that occurs as a result of increased blood glucose levels beyond the normal level.
Mellitus is a Latin name for “honey sweet”. The disease was identified by some Indian physicians and described as ‘honey urine’ because the urine was said to attracts ants.
Before you eat your blood glucose levels should range from 4.0 to 5.4 mmol/L (72 to 99 mg/dL). Two hours after eating your blood glucose levels should range from 5.4 to 7.8 mmol/L (99 to 140 mg/dL). Above this means that you have prediabetes or diabetes.
Almost all the food we eat is converted into glucose to be used by the body as fuel to obtain energy. Glucose is made in the liver and the muscles. The pancreas is an organ located between the stomach and the spine and helps in the digestion of food.
The pancreas releases a hormone called insulin that transports blood glucose to the body tissues and cells to be used as fuel for energy.
High blood glucose means that the pancreas is not producing enough insulin or the insulin produced is not sensitive to the body cells and tissues leading to diabetes or prediabetes.
Prediabetes is when the blood glucose level increases but not to a level that can cause diabetes. That is from 5.5 to 6.9 mmol/L or 100 to 125 mg/dl before food and 7.8 to 11.0 mmol/L or 140 to 199 mg/dl two hours after food. Above this range means that you have diabetes mellitus.
If you have prediabetes the chances of getting type two diabetes, stroke and heart disease are higher. You can delay or prevent type two diabetes and you can even return to normal blood glucose levels without taking any medicines only if you maintain a regular daily exercise and a healthy diet plan.
Having too much blood glucose for a long period can damage parts of the body such as the heart, blood vessels, kidney, eye and nerves.
WHAT CAUSES DIABETES MELLITUS?
Improper diet plan. Excessive intake of carbohydrate ‑ containing foods such as cassava, maize, rice, etc. increases the blood glucose levels since carbohydrates are mainly converted into glucose to be used by the body cells and tissues as fuel.
Such foods should be eaten moderately. It is therefore advisable to consume more of proteins and vegetables.
Indigestion leading to weight gain. Sleeping just after eating leads to improper digestion leaving the body with no option but to convert the undigested food into fats which are stored in the tissues of the body. Excess fats in the body causes insulin resistance. Insulin transports blood glucose to the body tissues and cells to be used as fuel.
Lack of regular exercise. Exercise helps to regulate weight gain by burning fats in the body.
Family diabetes history. Research has shown that individuals affected with diabetes have at least one close member of a particular family with the disease such as parents, therefore it is advisable to know your family history. If your family history shows consistency of diabetes, then there is a probability of you having diabetes.
HOW DO YOU PREVENT DIABETES MELLITUS?
Consult a dietician to plan a healthy eating plan for you and ensure that the eating plan is followed every day.
Maintain a regular exercise every day to be physically active.
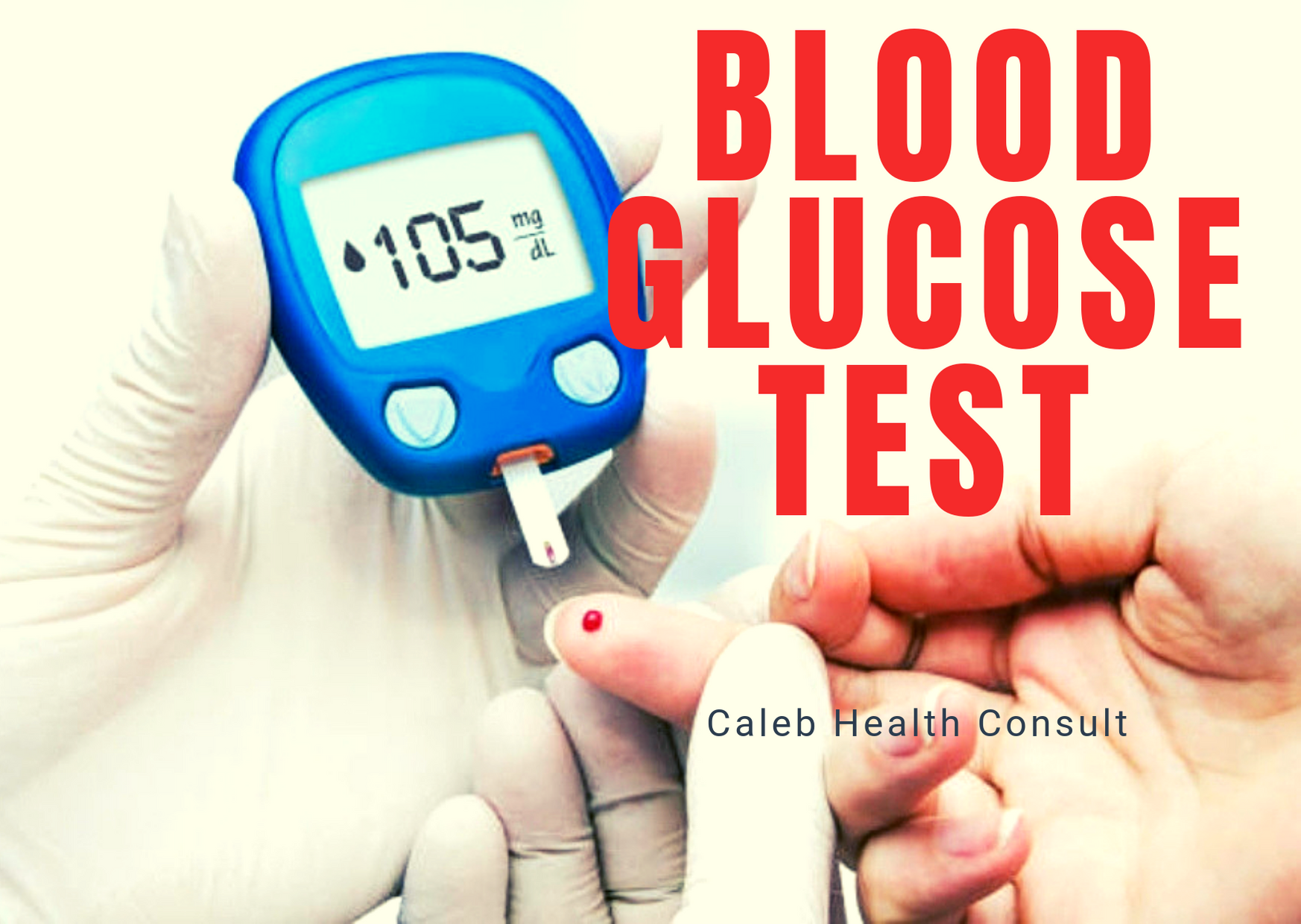
Regularly check your blood glucose level every day. If possible, acquire the blood glucose checking device(glucometer) and the test strips as well for regular checking.
WHAT ARE THE SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS OF DIABETES MELLITUS?
The signs and symptoms of diabetes mellitus are:







Sometimes individuals might not develop any of the above signs and symptoms so the only way to know is to constantly check your blood glucose level at the community pharmacy or hospital or better still acquire the glucose checking device(glucometer) at home for regular checking.
WHAT IS TYPE ONE DIABETES MELLITUS?

Type one diabetes mellitusmostly occurs in young people and can also occur in adults.
Onset is usually below 30 years of age. In this type of diabetes, the body does not make insulin or enough insulin. In this case exogenous insulin (insulin not produced in the body) is injected.
Sometimes the body’s immune system which is supposed to protect the body from virus, bacteria and other harmful substances attacks the body and damages certain cells and tissues in the body.
In type one diabetes mellitus the immune system destroys the cells that make insulin. Research is still ongoing to actually understand why the immune system sometimes attacks and damages the body.
HOW DO YOU TREAT TYPE ONE DIABETES MELLITUS?
Taking injections of insulin.
Regular exercise.
Checking your diet or consulting a dietician.
Controlling your blood pressure levels (blood pressure is the force of blood flow inside your vessels) by reducing stress, controlling your cholesterol levels etc.
Note that you must always eat before injecting your insulin to prevent hypoglycemia (low levels of blood glucose).
This is because the injected insulin immediately transport blood glucose to the body cells and tissues so if you inject the insulin on an empty stomach your blood glucose level will drop below normal which is very dangerous.
WHAT IS TYPE TWO DIABETES MELLITUS?

Type two diabetes mellitus usually occurs in adults. However, people who are overweight and lack regular exercise are at risk of developing type two diabetes mellitus. Onset is usually above 40 years of age.
In type two diabetes the pancreas does not make enough insulin and the little insulin produced by the pancreas is not sensitive to the body cells and tissues causing the blood glucose levels to increase beyond normal.
HOW DO YOU TREAT TYPE TWO DIABETES MELLITUS?
Taking medications such as glibenclamide (daonil), glimepiride (amaryl), gliclazide (diamicron), etcto cause the pancreas to produce more insulin and also metformin to cause the insulin to be sensitive to the body cells and tissues.
Drinking a lot of water to prevent dehydration since there is frequent urination. This is because the kidney eliminates more of the blood glucose through urine.
Controlling your blood cholesterol levels by seeking help from a dietician to design a food menu to reduce your blood cholesterol.
Controlling your blood pressure by reducing stress and undertaking regular exercise.
Note to always take your medicines after food or with food and eat always. Do not wait to be hungry or thirsty before eating or drinking water to prevent hypoglycemia (low levels of blood glucose) and dehydration (loss of water).
WHAT ARE THE SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS OF LOW LEVELS OF BLOOD GLUCOSE?
Signs that show an individual’s blood glucose levels are low (hypoglycemia) include:
Excessive hunger.
Dizziness or shakiness.
Confusion.
Being pale
Body weakness.
Excessive Sweating.
Anxiety and moodiness.
Headaches.
Rapid heartbeat.
Unexplained weight loss.
WHAT ARE THE SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS OF HIGH LEVELS OF BLOOD GLUCOSE?
Body weakness.
Headaches.
Confusion.
Excessive thirst.
Frequent urination.
Blurred vision.
Difficulty concentrating.
Slow healing wounds.
WHAT IS GESTATIONAL DIABETES MELLITUS?

Gestational diabetes mellitus is an increased level of blood glucose of a pregnant woman beyond normal.
Gestational diabetes mellitus normally goes away after birth.
In some cases, women who developed gestational diabetes mellitus during pregnancy are at risk of getting type two diabetes mellitus.
This is because during pregnancy, hormones are produced which causes insulin resistance.
A baby born to a woman who develop gestational diabetes mellitus during pregnancy is at risk of developing type two diabetes mellitus and also becoming obese.
WHAT CAUSES GESTATIONAL DIABETES MELLITUS?
Lack of healthy diet plan. Generally pregnant women consume a lot of food due to increased levels of appetite. Not following a healthy diet plan increases the blood glucose level beyond normal causing gestational diabetes mellitus.
Insulin resistance during pregnancy. All women have insulin resistance late in their pregnancy. This is because naturally pregnant women produce hormone which causes insulin resistance.

WHAT ARE THE SYMPTOMS OF GESTATIONAL DIABETES MELLITUS?
Gestational diabetes may not have any symptoms or the symptoms may be mild such as:
Excessive urinating,
Being thirstier than normal.
WHY MUST YOU TREAT YOUR DIABETES MELLITUS BEFORE GETTING PREGNANT?
It is advisable to maintain your blood glucose to a normal level for your safety and that of the baby before getting pregnant. High blood glucose can harm your baby during the first week of pregnancy even before knowing.
According to the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, a baby’s organs such as heart, lung, brain, kidney, start forming during the first eight weeks of pregnancy. Therefore:
High blood glucose levels can be harmful during this early stage and can increase the chance that your baby will have birth defects such as heart defects or defects of the brain or spine.
High blood glucose levels during pregnancy will increase the chance of your baby being born early, increase the weight of your baby or have breathing problems or low blood glucose right after birth.
Also high blood glucose levels can increase the chance of having miscarriage or still birth. Still birth is when the baby dies in the womb during the second trimester of the pregnancy.
HOW DO YOU MANAGE GESTATIONAL DIABETES MELLITUS?

Gestational diabetes mellitus can be managed by checking your diet to reduce weight before getting pregnant.
Regular exercise before and during pregnancy; if not then medicines are used for effective results.
WHAT PROBLEMS ARE ASSOCIATED WITH UNCONTROLLED GESTATIONAL DIABETES MELLITUS?
Uncontrolled gestational diabetes mellitus can lead to problems for both the mother and the baby.
Below are some of the problems that uncontrolled gestational diabetes can bring to the baby and the mother.
Baby
The baby can develop low blood glucose after birth. This is due to high insulin production in the baby. Intravenous glucose solutions can be used to bring the baby’s blood glucose levels to normal.
The baby grows very large. High blood glucose levels cause the baby’s pancreas to make excess insulin to transport glucose to the cells and tissues of the body. Such babies require cesarean section to be removed.
The baby can die before or shortly after birth.
Babies of mothers who developed gestational diabetes are at risk of developing type two diabetes later in life.
Mother
Pregnant women who once developed gestational diabetes in one pregnancy are likely to have it again in other pregnancies and even develop type two diabetes later in life.
Gestational diabetes causes preeclampsia. This is a condition characterized by high blood pressure.
HOW DO YOU MANAGE YOUR DIABETES MELLITUS?
Managing your diabetes mellitus is very important for a prolonged life. Below are some of the things to do as a diabetic patient.
Take your diabetes drugs regularly and on time.
Purchase the blood glucose level checking machine (glucometer) to constantly check your blood glucose level. There is a table below illustrating the blood glucose ranges and the meaning.
Maintain a healthy diet plan. Consult your dietician to design a healthy diet plan for you.
Do not wait to be thirsty before you drink water to prevent dehydration. Constantly drink a reasonable quantity of water at every point in time throughout the day. This is because as a diabetic patient your kidney constantly gets rid of the elevated levels of blood glucose causing you to urinate frequently losing a lot of water.
Do not wait to be hungry before you eat. Antidiabetic drugs cause insulin to transport blood glucose to the cells and tissues to be used as fuel for energy.
Therefore, you need to eat at every point in time throughout the day to prevent low levels of blood glucose(hypoglycemia).
Note: food without antidiabetic drugs, your blood glucose level as a diabetic patient becomes extremely high, antidiabetic drugs without food drops your blood glucose level below normal causing low levels of blood glucose which is very dangerous. Therefore, food and antidiabetic drugs are needed to manage your diabetes.
Maintain a regular daily exercise to prevent accumulation of fluid in your body parts such as your legs. This is because diabetes causes poor blood circulation. When blood do not circulate well in your body they accumulate in your body parts causing other health problems. Exercise enhances blood circulation.
WHAT ARE THE PROBLEMS ASSOCIATED WITH LONG TERM DIABETES MELLITUS? 
If you have diabetes for a long time and you do not control your blood glucose level, you are likely to develop the problems associated with diabetes.
Therefore, it is advisable that as soon as you are diagnosed of diabetes, you should take the necessary measures to control your blood glucose level.
The measures are to have a healthy diet plan, regular exercise and take your drugs regularly for effective results.
If you are diagnosed of prediabetes, having a healthy diet plan and regular exercise is enough to stabilize your blood glucose level to normal.
Below are some of the problems associated with diabetes.
Kidney damage. The kidneys contain numerous tiny blood vessels that filter waste substance from the blood. Diabetes can damage these blood vessels causing severe kidney failure which requires immediate kidney transplant or dialysis.
Dialysis is a process where waste substances are filtered from the body through a machine. This is because the kidney is not capable of filtering the blood. The kidney is responsible for filtering waste substances that are not needed from the blood.
Eye damage. The eye has several blood vessels that nourishes the eye with blood. Diabetes can damage these blood vessels leading to blindness. Diabetes can also increase the risk of other eyes condition such as cataracts and glaucoma.
Skin conditions. Diabetes can make the skin vulnerable to skin infections.
Difficulty in hearing. Research is still ongoing to actually determine how diabetes cause difficulty in hearing but from the basic knowledge on how diabetes damages nerves, some theories suggest that diabetes destroys the blood vessels that supplies blood to the nerves of the ears. Depression. This is associated with both type one and two diabetes.
Nerve damage. Diabetes can damage the blood vessels that supplies blood to the nerves causing you to lose your sense of feeling.
Cardiovascular diseases. Diabetes damages the blood vessels and also slows down circulation by making the blood thicker than normal. This puts pressure on the heart to contract more in order to supply blood to all parts of the body causing heart attacks, edema (accumulation of fluid in the legs due to poor circulation) and stroke. Stroke because some of the body parts are deprived of blood.
Foot damage. Diabetes damages the blood vessels that supplies blood to the foot. This deprives the cells and tissues in the foot of blood destroying the cells and tissues in the foot.
HOW DO YOU MANAGE YOUR DIABETES MELLITUS WHEN YOU ARE SICK?
When you are sick, your body’s defense system (immune system) fights against the pathogenic organisms (harmful organisms) that you have been infected with.
This causes your blood glucose levels to increase since more energy is needed by the body to get rid of the organism.
People who are sick sometimes are not able to eat leading to low levels of blood glucose which is very dangerous.
What to do in such situations:
Visit the community pharmacy or the hospital to receive immediate treatment.
Drink a lot of water to prevent dehydration. This is because the kidney gets rid of the excess glucose by producing more urine.
Try as possible to eat well. drink a lot of soup, yogurt etc.
Check your blood glucose level at least four times in a day and write down your results to be shown to your doctor.
Continue taking your diabetes medicine.
WHAT ARE THE LIST OF FOODS FOR BOTH TYPE ONE AND TYPE TWO DIABETES MELLITUS?
To be able to maintain a healthy diet for your diabetes you should understand how different types of foods affect your blood glucose levels.
Carbohydrates in foods such as grain, bread, yam, cassava etc are broken down faster into blood glucose than any type of food raising the blood glucose levels.
Proteins and fats do not directly increase blood glucose but both must be eaten moderately to maintain calories and weight in a healthy range.
Uncontrolled diabetes increases the risks of developing several serious diseases; however, eating foods that help to maintain blood glucose levels can reduce the risks of developing serious complications.
Fish such as salmon is one of the healthiest foods. It is rich in omega 3 fatty acids which has great health benefits. These foods are very important for diabetics who are likely to develop heart diseases and stroke.
Leafy green vegetables are very nutritious and low in calories. They protect the eyes from macular degeneration and cataracts which are common diabetes complications.
Cinnamon can lower blood glucose levels and improve insulin sensitivity.
Eggs help to maintain blood glucose levels to normal. It also improves insulin sensitivity and several other health benefits. Always eat the whole egg because the yolk contains the nutrients for its health benefits.
Apple cider vinegar has been shown to improve insulin sensitivity. Garlic helps to lower blood glucose levels and other several health benefits.
NOTE: Include protein in every meal you eat Avoid processed foods.
Less of your diet should be made up of fats. Include vegetables etc Eat less carbohydrate‑containing foods.
Consult a dietician to help you with a food menu to suit your financial status.
WHAT ARE THE LIST OF FOODS TO AVOID AS A DIABETIC PATIENTS?
Sugary drinks.
French fries.
Processed meat.
Frozen pizza.
Potatoes.
Cornflakes and highly processed high
sugar cereals.
White bread.
Nachos.
White pasta.
Store bought cakes, cookies, and sweets.
Deep fried foods.
Canned vegetables and beans.
Deep fried meats, such as chicken wings.
Bacon.
Canned vegetables and beans.
Fatty dairy products, such as full fat yoghurt, cheese, and cream.
Blood glucose levels must be checked from time to time in order to maintain a normal blood glucose range.
It is advisable to have the glucometer (a device for checking blood glucose levels) at home for constant checking.
It is always important to take care of your diabetes because overtime diabetes can lead to serious problems with your blood vessels, heart, nerves, kidneys, mouth, eyes, and feet.
This can lead to amputation of the body parts such as toe, leg etc.
Corresponding Author: Caleb Doamekpor, School of Pharmacy, Central University, Ghana.
Mobile: 0248391417.
Email Address: doamekporcaleb@gmail.com
Acknowledgements: This article was reviewed by peace doe, department of pharmacology and toxicology school of pharmacy central university, Ghana, Pharmacist Ellen Anthony-Williams and Pharmacist Emmanuel Fiadzorgbe, Top Up Retail Pharmacy, Ghana.
Reference: http://www.diabetes.niddk.nih.gov retrieved on February 20, 2019. 9: 30 PM.






















