Did you know diabetes mellitus is a major cause of blindness, kidney failure, heart attacks, lower limb amputation and stroke?
Globally an estimated 422 million adults are living with diabetes mellitus according to the world health organization (WHO) 2016.
It will be so helpful to know what diabetes mellitus is and how to manage your blood glucose level to prevent the serious problems associated with diabetes mellitus. The more knowledge you have about diabetes mellitus the better you will be able to manage it for a healthy life. I will entreat you to share this information with everyone to equip them with the necessary knowledge about diabetes mellitus and its management.
WHAT IS DIABETES MELLITUS?
Diabetes mellitus is a disease that occurs as a result of increased blood glucose levels beyond the normal level.
Mellitus is a Latin name for “honey sweet”. The disease was identified by some Indian physicians and described as ‘honey urine’ because the urine was said to attracts ants.
Before you eat your blood glucose levels should range from 4.0 to 5.4 mmol/L (72 to 99 mg/dL). Two hours after eating your blood glucose levels should range from 5.4 to 7.8 mmol/L (99 to 140 mg/dL). Above this means that you have prediabetes or diabetes.
Almost all the food we eat is converted into glucose to be used by the body as fuel to obtain energy. Glucose is made in the liver and the muscles. The pancreas is an organ located between the stomach and the spine and helps in the digestion of food.
The pancreas releases a hormone called insulin that transports blood glucose to the body tissues and cells to be used as fuel for energy.
High blood glucose means that the pancreas is not producing enough insulin or the insulin produced is not sensitive to the body cells and tissues leading to diabetes or prediabetes.
Prediabetes is when the blood glucose level increases but not to a level that can cause diabetes. That is from 5.5 to 6.9 mmol/L or 100 to 125 mg/dl before food and 7.8 to 11.0 mmol/L or 140 to 199 mg/dl two hours after food. Above this range means that you have diabetes mellitus.
If you have prediabetes the chances of getting type two diabetes, stroke and heart disease are higher. You can delay or prevent type two diabetes and you can even return to normal blood glucose levels without taking any medicines only if you maintain a regular daily exercise and a healthy diet plan.
Having too much blood glucose for a long period can damage parts of the body such as the heart, blood vessels, kidney, eye and nerves.
WHAT CAUSES DIABETES MELLITUS?

Improper diet plan. Excessive intake of carbohydrate ‑ containing foods such as cassava, maize, rice, etc. increases the blood glucose levels since carbohydrates are mainly converted into glucose to be used by the body cells and tissues as fuel.
Such foods should be eaten moderately. It is therefore advisable to consume more of proteins and vegetables.
Indigestion leading to weight gain. Sleeping just after eating leads to improper digestion leaving the body with no option but to convert the undigested food into fats which are stored in the tissues of the body. Excess fats in the body causes insulin resistance. Insulin transports blood glucose to the body tissues and cells to be used as fuel.
Lack of regular exercise. Exercise helps to regulate weight gain by burning fats in the body.
Family diabetes history. Research has shown that individuals affected with diabetes have at least one close member of a particular family with the disease such as parents, therefore it is advisable to know your family history. If your family history shows consistency of diabetes, then there is a probability of you having diabetes.
HOW DO YOU PREVENT DIABETES MELLITUS?
Consult a dietician to plan a healthy eating plan for you and ensure that the eating plan is followed every day.
Maintain a regular exercise every day to be physically active.
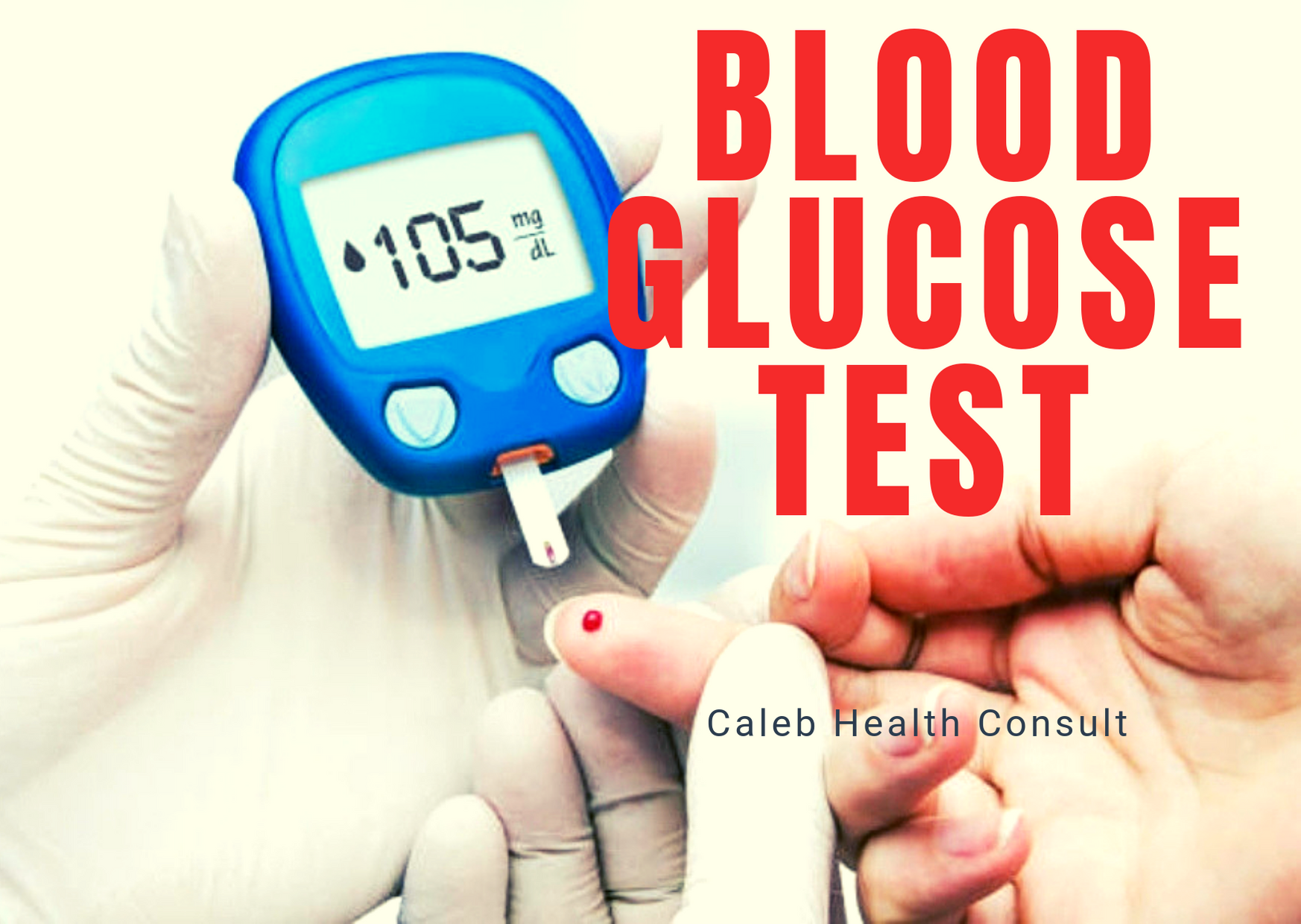
Regularly check your blood glucose level every day. If possible, acquire the blood glucose checking device(glucometer) and the test strips as well for regular checking.
WHAT ARE OF THE SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS OF DIABETES MELLITUS?
The signs and symptoms of diabetes mellitus are:







Sometimes individuals might not develop any of the above signs and symptoms so the only way to know is to constantly check your blood glucose level at the community pharmacy or hospital or better still acquire the glucose checking device(glucometer) at home for regular checking.
Corresponding Author: Caleb Doamekpor, School of Pharmacy, Central University, Ghana.
Mobile: 0248391417.
Email Address: doamekporcaleb@gmail.com
Acknowledgements: This article was reviewed by Peace Doe, department of pharmacology and toxicology school of pharmacy central university, Ghana, Pharmacist Ellen Anthony-Williams and Pharmacist Emmanuel Fiadzorgbe, Top Up Retail Pharmacy, Ghana.
Reference: http://www.diabetes.niddk.nih.gov retrieved on February 20, 2019. 9: 30 PM.
Episode Two will be released tomorrow, November 5, 2019 at 1: 00 pm.
Episode two will highlight on Type one diabetes, Type two diabetes and the signs and symptoms of low and high blood glucose levels.
